https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-024-00469-w
Regular Article – Soft Matter
Structural analysis of physical gel networks using graph neural networks
1
Institut für Theoretische Physik 1, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, 91058, Erlangen, Bavaria, Germany
2
Max-Planck Institut für Physik, 85748, Garching, Bavaria, Germany
Received:
16
August
2024
Accepted:
21
December
2024
Published online:
13
January
2025
We employ graph neural networks (GNN) to analyse and classify physical gel networks obtained from Brownian dynamics simulations of particles with competing attractive and repulsive interactions. Conventionally such gels are characterized by their position in a state diagram spanned by the packing fraction and the strength of the attraction. Gel networks at different regions of such a state diagram are qualitatively different although structural differences are subtile while dynamical properties are more pronounced. However, using graph classification the GNN is capable of positioning complete or partial snapshots of such gel networks at the correct position in the state diagram based on purely structural input. Furthermore, we demonstrate that not only supervised learning but also unsupervised learning can be used successfully. Therefore, the small structural differences are sufficient to classify the gel networks. Even the trend of data from experiments with different salt concentrations is classified correctly if the GNN was only trained with simulation data. Finally, GNNs are used to compute backbones of gel networks. As the node features used in the GNN are computed in linear time 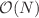 , the use of GNN significantly accelerates the computation of reduced networks on a particle level.
, the use of GNN significantly accelerates the computation of reduced networks on a particle level.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.





