https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-024-00470-3
Regular Article - Flowing Matter
Simulation of a liquid drop on a soft substrate
Department of Fundamental Physics, Faculty of Physics, Alzahra University, 1993891167, Tehran, Iran
Received:
8
July
2024
Accepted:
21
December
2024
Published online:
21
January
2025
A liquid drop resting on a soft substrate is numerically simulated as an energy minimization problem. The elastic substrate is modeled as a cubic lattice of mass-springs, to which an energy term controlling the change of volume is associated. The interfacial energy between three phases of solid, liquid, and vapor is also introduced. Under the constant volume constraint of the liquid drop, the total energy of the system is subjected to a numerical minimization process by which profiles of both substrate and drop are obtained. The numerical simulation enables the modeling of the wetting setup with various parameters associated with solid and liquid phases, including the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the solid, the surface tension of the three phases, and geometrical parameters such as the contact radius or thickness of the solid. The direct outputs of the minimization process are the displacements of the solid lattice and boundary points of the liquid, by which the behavior of all relevant quantities, such as contact angles in the three phases, as well as the effective surface tension of the solid, can be quantitatively studied. The resulting displacements of the solid are compared with the exact solution of the elasticity equation under the assumption of no tangential traction, and a quite satisfactory agreement is observed. However, at larger Young’s modulus or lower Poisson’s ratios the agreement between the numerical results and the analytical solutions is lost in the vicinity of the contact points. Interestingly, a non-zero tangential traction in the vicinity of contact points is calculated by the numerical outputs, indicating that the assumption of zero tangential traction is not valid generally around the contact points. The effective surface tension at the contact points is calculated for an incompressible solid substrate, showing a linear increase with respect to the Young’s modulus of the solid, as 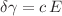 .
.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





