https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-021-00071-4
Regular Article - Soft Matter
Analysis of purification of charged giant vesicles in a buffer using their size distribution
Department of Physics, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), 1000, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Received:
27
January
2021
Accepted:
13
April
2021
Published online:
28
April
2021
We have analyzed the purification of charged giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) prepared in a buffer containing various concentrations of salt using their size distribution. The membranes of GUVs were synthesized by a mixture of dioleoylphosphocholine (DOPC) and dioleoylphosphatidylglycerol (DOPG) lipids. The DOPG mole fractions (X) in the membranes of GUVs were 0.10, 0.25, 0.40, 0.55, 0.70, 0.90 in a physiological buffer containing 162 mM salt. In addition, for a fixed value of X the concentrations of salt (C) in the buffer were 12, 62, 112, 162, 212, 312, 362 mM. The size distribution histograms of experimentally investigated unpurified and purified GUVs were fitted with the lognormal distribution and obtained the multiplication factor 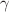 for mean (
for mean (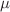 ) and
) and  for standard deviation (
for standard deviation ( ) of the lognormal distribution. The key parameters
) of the lognormal distribution. The key parameters 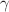 and
and 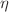 were responsible for changing the average size and size distribution of unpurified GUVs to purified ones. The theoretically fitting equation of experimentally obtained X- and C-dependent values of
were responsible for changing the average size and size distribution of unpurified GUVs to purified ones. The theoretically fitting equation of experimentally obtained X- and C-dependent values of 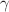 and
and 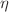 provided the calibration equation for estimating the average size of purified GUVs theoretically for any values of X and C. The estimated size of purified GUVs increased with the increase in electrostatic effect (i.e., increase in vesicle surface charge density or decrease in salt concentration in buffer). The estimated size of purified GUVs varied with X and C, which supported the previous report qualitatively. These investigations might be helpful in the field of cell/chemical biology for understanding the process of purification of vesicles/cells investigated by any other techniques.
provided the calibration equation for estimating the average size of purified GUVs theoretically for any values of X and C. The estimated size of purified GUVs increased with the increase in electrostatic effect (i.e., increase in vesicle surface charge density or decrease in salt concentration in buffer). The estimated size of purified GUVs varied with X and C, which supported the previous report qualitatively. These investigations might be helpful in the field of cell/chemical biology for understanding the process of purification of vesicles/cells investigated by any other techniques.
Marzuk Ahmed and Mohammad Abu Sayem Karal have contributed equally.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021





