https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-022-00160-y
Regular Article - Soft Matter
Configurational entropy of a finite number of dumbbells close to a wall
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Polymer Technology, Eindhoven University of Technology, PO Box 513, 5600, Eindhoven, MB, The Netherlands
Received:
9
September
2021
Accepted:
5
January
2022
Published online:
24
January
2022
The effect of confinement on the conformation of N dumbbells in D dimensions close to a non-interacting and rigid flat wall is examined. Using statistical mechanics and numerical calculations, the partition coefficient and the confinement-induced change in the configurational entropy are calculated as a function of the conformation tensor  and of the distance of the dumbbells from the wall. Analytical predictions and numerical results for
and of the distance of the dumbbells from the wall. Analytical predictions and numerical results for  concerning the behavior close to the limiting cases (onset of and saturation of confinement) agree favorably; in one case where an analytical prediction has not been achieved, a thorough numerical study establishes the limiting behavior nevertheless. Beyond these limiting cases, the overall behavior of the partition coefficient and the configurational entropy has been examined as well in detail, for various choices of the parameters. Furthermore, it is shown that the effect of confinement for
concerning the behavior close to the limiting cases (onset of and saturation of confinement) agree favorably; in one case where an analytical prediction has not been achieved, a thorough numerical study establishes the limiting behavior nevertheless. Beyond these limiting cases, the overall behavior of the partition coefficient and the configurational entropy has been examined as well in detail, for various choices of the parameters. Furthermore, it is shown that the effect of confinement for 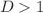 is captured entirely by the partition coefficient determined for
is captured entirely by the partition coefficient determined for  . In general, the average extension of the dumbbells in the direction perpendicular to the wall is decreased the closer the dumbbells are to the wall. Also, the decay of the partition coefficient with increasing extension of the dumbbells becomes steeper, i.e., more localized, the higher the number of dumbbells N. Finally, it is discussed under what conditions these results can be used also for the case of slab- (i.e., slit-) confinement.
. In general, the average extension of the dumbbells in the direction perpendicular to the wall is decreased the closer the dumbbells are to the wall. Also, the decay of the partition coefficient with increasing extension of the dumbbells becomes steeper, i.e., more localized, the higher the number of dumbbells N. Finally, it is discussed under what conditions these results can be used also for the case of slab- (i.e., slit-) confinement.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.





