https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11887-6
Regular Article
Relaxation dynamics and crystallization study of glass-forming chiral-nematic liquid crystal S,S-2,7-bis(4-pentylphenyl)-9,9-dimethylbutyl 9H-fluorene (5P-Am*FLAm*-P5)
1
Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, ul. Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342, Kraków, Poland
2
Institute of Chemistry, Military University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland
* e-mail: Malgorzata.Jasiurkowska-Delaporte@ifj.edu.pl
Received:
27
May
2019
Accepted:
9
August
2019
Published online:
11
September
2019
The chiral nematic S,S-2,7-bis(4-pentylphenyl)-9,9-dimethylbutyl9H-fluorene (5P-Am*FLAm*-P5) liquid crystal shows a complex phase diagram strongly dependent on thermal treatment as identified by Polarizing Optical Microscopy (POM) and differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). The molecular dynamics in various thermodynamics states was studied by means of broadband dielectric spectroscopy (BDS). The vitrification of a chiral nematic phase (N
*) is manifested by a Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann (VFT)-type temperature dependence of structural relaxation time (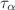 ). Three dielectric relaxation processes exhibiting Arrhenius-like thermal activation were found in conformationally disordered (condis) Cr1 and Cr2 structures. The isothermal cold crystallization process of Cr2 occurs in the metastable N
* phase; however, in the non-isothermal experiments, the Cr2 phase is formed in the isotropic phase obtained on heating the metastable N
* phase. The findings for the isothermal process were compared with those regarding non-isothermal crystallization.
). Three dielectric relaxation processes exhibiting Arrhenius-like thermal activation were found in conformationally disordered (condis) Cr1 and Cr2 structures. The isothermal cold crystallization process of Cr2 occurs in the metastable N
* phase; however, in the non-isothermal experiments, the Cr2 phase is formed in the isotropic phase obtained on heating the metastable N
* phase. The findings for the isothermal process were compared with those regarding non-isothermal crystallization.
Key words: Topical issue: Dielectric Spectroscopy Applied to Soft Matter
© The Author(s), 2018





