https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11767-1
Regular Article
Ultrasound transmission through monodisperse 2D microfoams
1
Gulliver, CNRS, ESPCI Paris, PSL Research University, 10 rue Vauquelin, 75005, Paris, France
2
Institut Jean Le Rond d’Alembert, CNRS, Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ. Paris 6, Paris, France
3
Laboratoire Matière et Systèmes Complexes, CNRS, Université Paris-Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
* e-mail: lorene.champougny@espci.psl.eu
** e-mail: juliette.pierre@upmc.fr
Received:
21
August
2018
Accepted:
21
December
2018
Published online:
21
January
2019
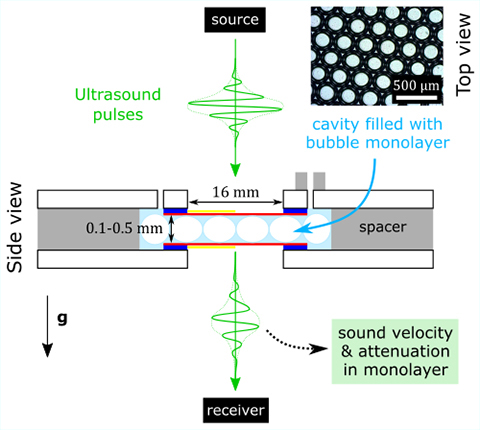
While the acoustic properties of solid foams have been abundantly characterized, sound propagation in liquid foams remains poorly understood. Recent studies have investigated the transmission of ultrasound through three-dimensional polydisperse liquid foams (Pierre et al., 2013, 2014, 2017). However, further progress requires to characterize the acoustic response of better-controlled foam structures. In this work, we study experimentally the transmission of ultrasounds through a single layer of monodisperse bubbles generated by microfluidics techniques. In such a material, we show that the sound velocity is only sensitive to the gas phase. Nevertheless, the structure of the liquid network has to be taken into account through a transfer parameter analogous to the one in a layer of porous material. Finally, we observe that the attenuation cannot be explained by thermal dissipation alone, but is compatible with viscous dissipation in the gas pores of the monolayer.
Key words: Soft Matter: Self-organisation and Supramolecular Assemblies
© EDP Sciences, SIF, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature, 2019