https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2012-12094-9
Regular Article
Rupture of multiple receptor-ligand bonds: Bimodal distribution of bond rupture force
University of Maryland Baltimore County, 21250, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
* e-mail: vkg@umbc.edu
Received:
26
March
2012
Revised:
16
July
2012
Accepted:
17
August
2012
Published online:
27
September
2012
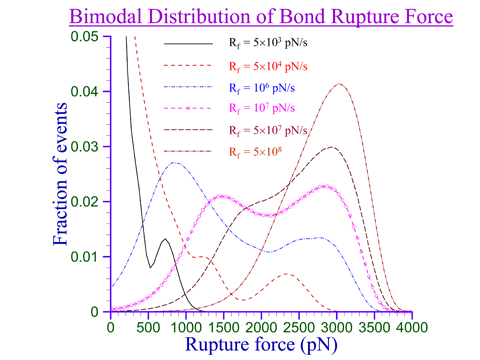
Monte Carlo simulation of the rupture of multiple receptor-ligand bonds between two PMN cells suspended in a Newtonian fluid is performed. In the presence of a hydrodynamic drag force acting on two PMN cells the interplay of multiple receptor-ligand bonds between these cells leads to a bimodal distribution of the bond rupture force at certain loading rates. Specifically, it is found that the interplay of multiple bonds between two PMN cells in the presence of hydrodynamic drag force acting on these cells modifies the bond energy landscape in such a way as to lead to a bimodal distribution of the bond rupture force where a low force peak switches to a high force peak as the loading rate is increased progressively, characteristics of two-state systems.
Key words: Living systems: Biological Matter
© EDP Sciences, SIF, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2012