https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-025-00504-4
Regular Article - Soft Matter
Linear dielectric spectroscopy of a polymer network stabilizing a ferroelectric liquid crystal
1
Faculté Des Sciences, Laboratoire SETIME, Université Ibn Tofail, Kenitra, Morocco
2
Unité de Dynamique Et Structure Des Matériaux Moléculaires, Université du Littoral Côte d’Opale, Dunkerque, France
3
Laboratoire de physique des matériaux et subatomique, Faculté des sciences, Kenitra, Morocco
Received:
19
March
2025
Accepted:
29
June
2025
Published online:
7
August
2025
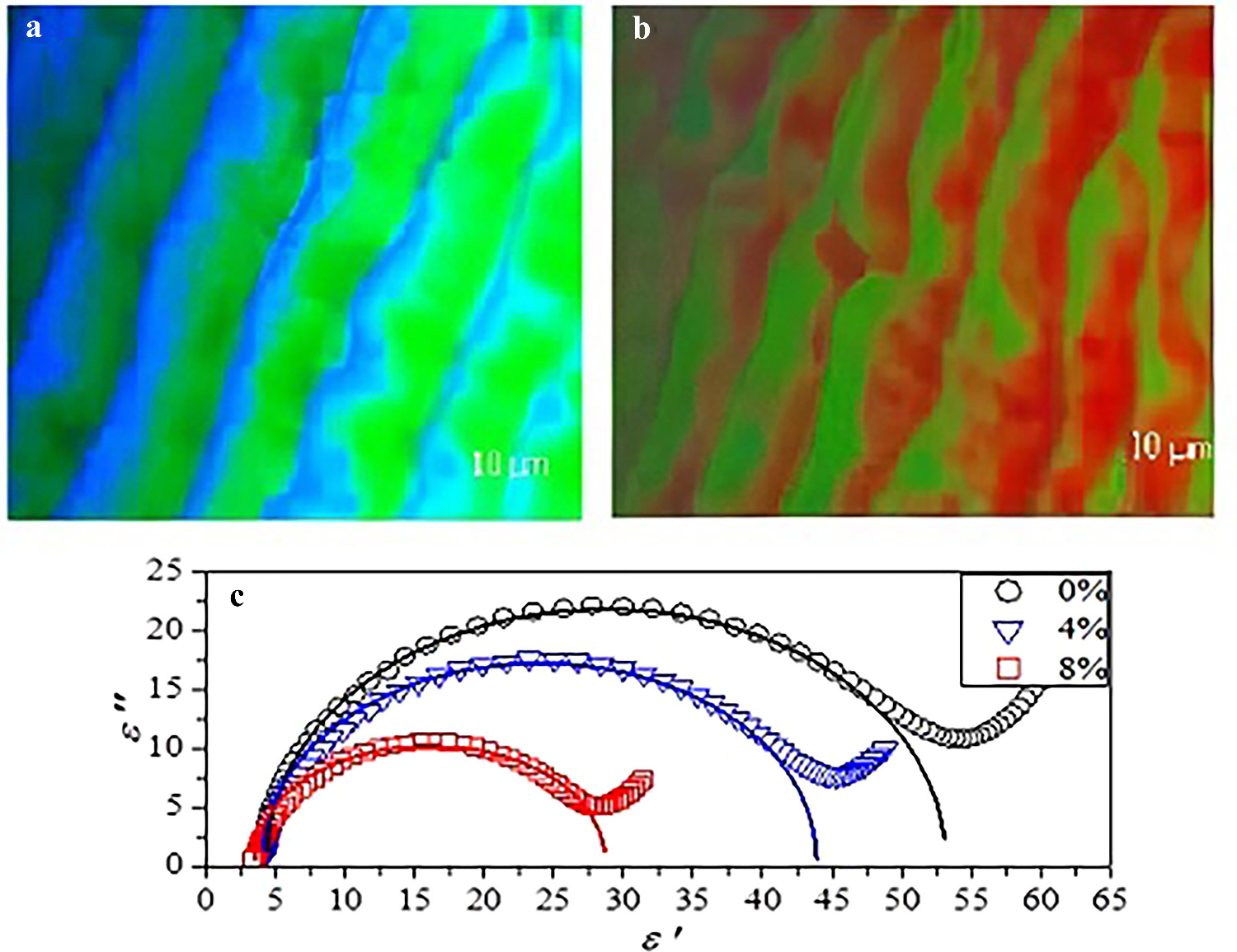
In this study, the linear dielectric characterization of a ferroelectric liquid crystal (FLC) stabilized by an anisotropic polymer network (PSFLC) was investigated. The liquid crystal employed in the PSFLC composites exhibited the chiral smectic C phase (SmC*), with a short helical pitch, a high tilt angle, and a high degree of spontaneous polarization. Dielectric spectroscopy was preceded by polarizing optical microscopy, as well as structural and electro-optical studies on pure FLC and PSFLC composites at different polymer concentrations. These studies enabled the determination of the pitch of the helix, the tilt angle, and the spontaneous polarization as a function of temperature and electric field. In the absence of a DC voltage, the dielectric response indicated the relaxation of the Goldstone mode as well as a reduction in tilt angle, spontaneous polarization and relaxation amplitude as the polymer density increased. By integrating the experimental data with the Landau model, the physical parameters, including the torsional elastic constant and rotational viscosity, were identified for pure FLC and PSFLC films. In addition, the impact of polymer density on these physical parameters was explored.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.