https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-025-00505-3
Regular Article - Soft Matter
Conformational properties of strictly two-dimensional equilibrium polymers
Institut Charles Sadron, Université de Strasbourg & CNRS, 23 rue du Loess, 67034, Strasbourg Cedex, France
a
joachim.wittmer@ics-cnrs.unistra.fr
Received:
4
June
2025
Accepted:
30
June
2025
Published online:
23
July
2025
Two-dimensional monodisperse linear polymer chains are known to adopt for sufficiently large chain lengths N and surface fractions 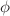 compact configurations with fractal perimeters. We show here by means of Monte Carlo simulations of reversibly connected hard disks (without branching, ring formation and chain intersection) that polydisperse self-assembled equilibrium polymers with a finite scission energy E are characterized by the same universal exponents as their monodisperse peers. Consistently with a Flory-Huggins mean-field approximation, the polydispersity is characterized by a Schulz–Zimm distribution with a susceptibility exponent
compact configurations with fractal perimeters. We show here by means of Monte Carlo simulations of reversibly connected hard disks (without branching, ring formation and chain intersection) that polydisperse self-assembled equilibrium polymers with a finite scission energy E are characterized by the same universal exponents as their monodisperse peers. Consistently with a Flory-Huggins mean-field approximation, the polydispersity is characterized by a Schulz–Zimm distribution with a susceptibility exponent 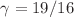 for all not dilute systems and the average chain length
for all not dilute systems and the average chain length 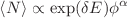 thus increases with an exponent
thus increases with an exponent 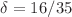 . Moreover, it is shown that
. Moreover, it is shown that 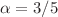 for semidilute solutions and
for semidilute solutions and 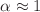 for larger densities. The intermolecular form factor F(q) reveals for sufficiently large
for larger densities. The intermolecular form factor F(q) reveals for sufficiently large 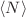 a generalized Porod scattering with
a generalized Porod scattering with 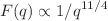 for intermediate wavenumbers q consistently with a fractal perimeter dimension
for intermediate wavenumbers q consistently with a fractal perimeter dimension 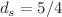 .
.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




