https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-024-00460-5
Regular Article - Living Systems
A study of novel linear Diophantine fuzzy topological numbers and their application to communicable diseases
1
Science and Medicine Foundation Centre, Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin, Gong Badak Campus, 21300, Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia
2
Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin, East Coast Environmental Research Institute (ESERI), Gong Badak Campus, 21300, Kuala, Terengganu, Malaysia
3
Department of Mathematics, Riphah International University, Lahore, Pakistan
4
Department of Solids and Structures, School of Engineering, The University of Manchester, M13 9PL, Manchester, UK
5
Department of Mathematics, Kips College Thokar Campus Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
6
Department of Mathematics, College of Science, King Saud University, P.O. Box 2455, 11451, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Received:
8
May
2024
Accepted:
1
November
2024
Published online:
1
December
2024
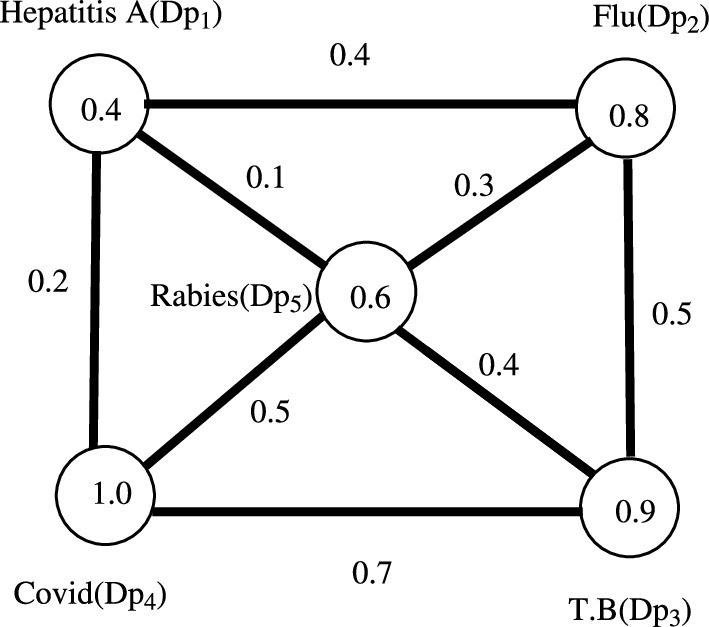
The idea of linear Diophantine fuzzy sets (LDFs) is a novel tool for analysis, soft computing, and optimization. Recently, the concept of a linear Diophantine fuzzy graph has been proposed in 2022. The aim of this research is to extend topological numbers to LDFSs. A real value assigned to a particular graph is known as a topological graph theoretic parameter. We extend the bound of the crisp graph toward the linear Diophantine fuzzy graph (LDFG), including the edge and vertex deletion operations via LDFG theoretic parameters. We also investigate the interesting bound of the LDFGs via LDFG theoretic parameters. Finally, for decision-making problems, we developed an algorithm by exploiting the relationship between LDFG theoretic parameters and LDFSs. Based on the established approach, we discussed a numerical example of an application of a medical diagnosis using the linear Diophantine fuzzy Sombor graph parameter and the first, fifth, and sixth versions of the linear Diophantine fuzzy Sombor graph parameters.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.