https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-024-00437-4
Regular Article - Flowing Matter
Analysis of the number of topological defects in active nematic fluids under applied shear flow
1
State Key Laboratory of Fluid Power Transmission and Control, Zhejiang University, 310027, Hangzhou, China
2
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center for the Safety of Pressure Vessel and Pipeline, Ningbo University, 315201, Ningbo, China
Received:
25
January
2024
Accepted:
31
May
2024
Published online:
20
June
2024
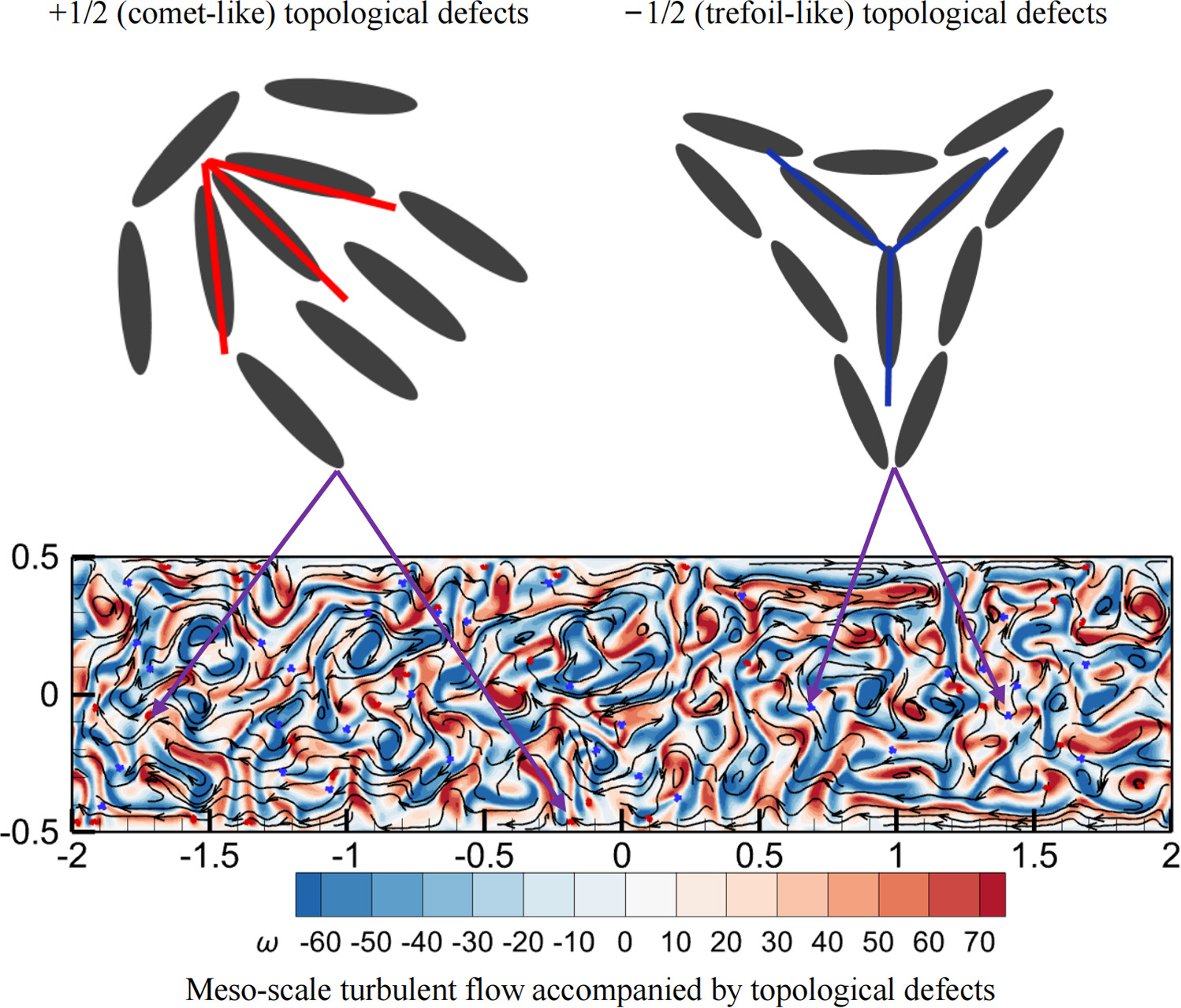
The number of topological defects in the shear flow of active nematic fluids is numerically investigated in this study. The evolution of the flow state of extensile active nematic fluids is explored by increasing the activity of active nematic fluids. Evidently, medium-activity active nematic fluids exhibit a highly ordered vortex lattice fluid state. However, high-activity active nematic fluids exhibit a meso-scale turbulent flow accompanied by topological defects. The number of topological defects (Ndef) increases with increasing shear Reynolds number (Res). Fluid viscosity strongly influences Ndef, while the influence of fluid density is relatively weak. Ndef decreases with increasing activity length scale (lζ) value. A small Res value strongly influences Ndef, whereas a large lζ value only weakly influences Ndef. As the activity increases, Ndef in contractile active nematic fluids becomes larger than that of extensile active nematic fluids.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.