https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-023-00376-6
Regular Article - Soft Matter
Effective interactions and phase behavior of protein solutions in the presence of hexamine cobalt(III) chloride
Institut für Angewandte Physik, Universität Tübingen, Auf der Morgenstelle 10, 72076, Tübingen, Germany
a
maximilian.senft@uni-tuebingen.de
d
fajun.zhang@uni-tuebingen.de
Received:
28
September
2023
Accepted:
9
November
2023
Published online:
5
December
2023
It is well established that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) exhibit a reentrant condensation (RC) phase behavior in the presence of the trivalent hexamine cobalt(III) cations (Hac) which can be important for their packing and folding. A similar behavior can be observed for negatively charged globular proteins in the presence of trivalent metal cations, such as Y3+ or La3+. This phase behavior is mainly driven by charge inversion upon an increasing salt concentration for a fixed protein concentration (cp). However, as Hac exhibits structural differences compared to other multivalent metal cations, with six ammonia ligands (NH3) covalently bonded to the central cobalt atom, it is not clear that Hac can induce a similar phase behavior for proteins. In this work, we systematically investigate whether negatively charged globular proteins β-lactoglobulin (BLG), bovine serum albumin (BSA), human serum albumin (HSA) and ovalbumin (OVA) feature Hac-induced RC. Effective protein–protein interactions were investigated by small-angle X-ray scattering. The reduced second virial coefficient (B2/B2HS) was obtained as a function of salt concentration. The virial coefficient analysis performed confirms the reentrant interaction (RI) behavior for BLG without actually inducing RC, given the insufficient strengths of the interactions for the latter to occur. In contrast, the strength of attraction for BSA, HSA and OVA are too weak to show RC. Model free analysis of the inverse intensity 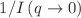 also supports this finding. Looking at different q-range by employing static (SLS) and dynamic light scattering experiments, the presence of RI behavior can be confirmed. The results are further discussed in view of metal cation binding sites in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), where Hac induced RC phase behavior.
also supports this finding. Looking at different q-range by employing static (SLS) and dynamic light scattering experiments, the presence of RI behavior can be confirmed. The results are further discussed in view of metal cation binding sites in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), where Hac induced RC phase behavior.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-023-00376-6.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.





