https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-023-00342-2
Regular Article – Soft Matter
Coarse-grained explicit-solvent molecular dynamics simulations of semidilute unentangled polyelectrolyte solutions
Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 37831, Oak Ridge, TN, USA
a
carrillojy@ornl.gov
c
kumarr@ornl.gov
d
sumpterbg@ornl.gov
Received:
22
May
2023
Accepted:
28
August
2023
Published online:
5
October
2023
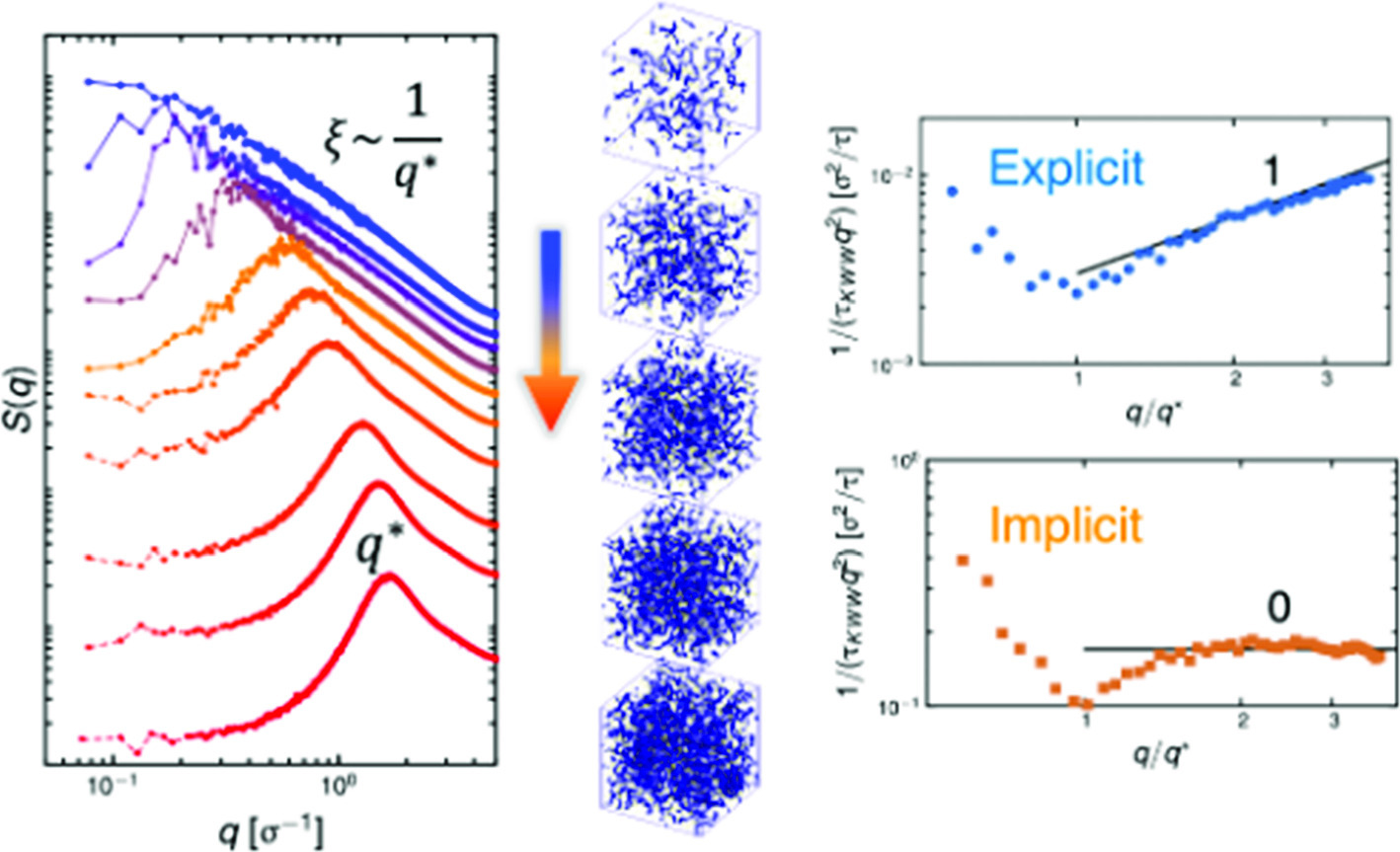
We present results from explicit-solvent coarse-grained molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of fully charged, salt-free, and unentangled polyelectrolytes in semidilute solutions. The inclusion of a polar solvent in the model allows for a more physical representation of these solutions at concentrations, where the assumptions of a continuum dielectric medium and screened hydrodynamics break down. The collective dynamic structure factor of polyelectrolytes, S(q, t), showed that at  , where
, where  is the polyelectrolyte peak in the structure factor S(q) and
is the polyelectrolyte peak in the structure factor S(q) and 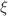 is the correlation length, the relaxation time obtained from fits to stretched exponential was
is the correlation length, the relaxation time obtained from fits to stretched exponential was 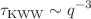 , which describes unscreened Zimm-like dynamics. This is in contrast to implicit-solvent simulations using a Langevin thermostat where
, which describes unscreened Zimm-like dynamics. This is in contrast to implicit-solvent simulations using a Langevin thermostat where 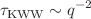 . At
. At 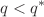 , a crossover region was observed that eventually transitions to another inflection point
, a crossover region was observed that eventually transitions to another inflection point 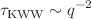 at length scales larger than
at length scales larger than 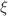 for both implicit- and explicit-solvent simulations. The simulation results were also compared to scaling predictions for correlation length,
for both implicit- and explicit-solvent simulations. The simulation results were also compared to scaling predictions for correlation length, 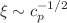 , specific viscosity,
, specific viscosity, 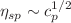 , and diffusion coefficient,
, and diffusion coefficient, 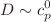 , where
, where 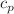 is the polyelectrolyte concentration. The scaling prediction for
is the polyelectrolyte concentration. The scaling prediction for 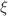 holds; however, deviations from the predictions for
holds; however, deviations from the predictions for 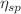 and D were observed for systems at higher
and D were observed for systems at higher 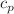 , which are in qualitative agreements with recent experimental results. This study highlights the importance of explicit-solvent effects in molecular dynamics simulations, particularly in semidilute solutions, for a better understanding of polyelectrolyte solution behavior.
, which are in qualitative agreements with recent experimental results. This study highlights the importance of explicit-solvent effects in molecular dynamics simulations, particularly in semidilute solutions, for a better understanding of polyelectrolyte solution behavior.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-023-00342-2.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Copyright comment corrected publication 2023
© EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.. corrected publication 2023