https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-023-00312-8
Regular Article - Soft Matter
On the origin of the negative energy-related contribution to the elastic modulus of rubber-like gels
1
Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV), Av. P. H. Rolfs, s/n, 36570-900, Viçosa, Brazil
2
Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia de Minas Gerais, Pç. José Emiliano Dias, 87, 35430-034, Ponte Nova, Brazil
Received:
8
February
2023
Accepted:
21
June
2023
Published online:
11
July
2023
We consider a coarse-grained polymer model in order to investigate the origin of a recently discovered negative energy-related contribution to the elastic modulus G(T) of rubber-like gels. From this model, we are able to compute an exact expression for the free energy of the system, which allows us to evaluate a stress–strain relationship that displays a non-trivial dependence on the temperature T. We validate our approach through comparisons between the theoretical results and the experimental data obtained for tetra-PEG hydrogels, which indicate that, although simple, the present model works well to describe the experiments. Importantly, our approach unveiled aspects of the experimental analysis which turned out to be different from the conventional entropic and energetic analysis broadly used in the literature. Also, in contrast to the linear dependence predicted by the traditional, i.e., purely entropic, models, our results suggest that the general expression of the elastic modulus should be of the form 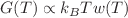 , with w(T) being a temperature-dependent correction factor that could be related to the interaction between the chains in the network and the solvent. Accordingly, the correction factor allows the expression found for the elastic modulus to describe both rubber and rubber-like gels.
, with w(T) being a temperature-dependent correction factor that could be related to the interaction between the chains in the network and the solvent. Accordingly, the correction factor allows the expression found for the elastic modulus to describe both rubber and rubber-like gels.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





