https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2007-10359-0
Regular Article
Modeling of a two-regime crystallization in a multicomponent lipid system under shear flow
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Waterloo, N2L 3G1, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
2
Department of Food Science, University of Guelph, N1G 2W1, Guelph, Ontario, Canada
* e-mail: Gianfranco.mazzanti@dal.ca
** e-mail: amarango@uoguelph.ca
*** e-mail: idziak@uwaterloo.ca
Received:
10
October
2007
Accepted:
15
July
2008
Published online:
29
August
2008
The kinetics of phase transitions of milk fat triacylglycerols, as model multicomponent lipid systems, were studied under shear in a Couette cell at 17 °C, 17.5 °C and 20 °C under shear rates ranging from 0 to 2880s^-1 using synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Two-dimensional diffraction patterns were captured during the crystallization process. No effect of shear on onset time for phase α from the liquid was observed. Afterwards a two-regime crystallization process was observed. During the first regime, as observed in other systems, shear reduced the onset time of the phase transition from phase α to 2880s−. The model previously developed for palm oil (ODE model) worked well to describe this regime, confirming the general value of the proposed ODE model. However, the ODE model did not satisfactorily describe the second regime. We found that, as the system gets closer to equilibrium, the growth regime becomes controlled by diffusion, manifested by the kinetics following a 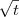 dependence. This regime was found to be consistent with a mechanism combining step growth at a kink with progressive selection of the crystallizing moieties. This mechanism is in agreement with the displacement of the diffraction peak positions, which revealed how increased shear rate promotes the crystallization of the higher melting fraction affecting the composition of the crystallites.
dependence. This regime was found to be consistent with a mechanism combining step growth at a kink with progressive selection of the crystallizing moieties. This mechanism is in agreement with the displacement of the diffraction peak positions, which revealed how increased shear rate promotes the crystallization of the higher melting fraction affecting the composition of the crystallites.
PACS: 81.10.Dn Growth from solutions – / 81.10.Jt Growth from solid phases (including multiphase diffusion and recrystallization) – / 61.05.cp X-ray diffraction –
© Springer, 2008




